VMware Cloud on AWS
VMware Cloud on AWS is a hybrid cloud service that runs the VMware software-defined data center (SDDC) stack in the AWS public cloud. This partnership between VMware and AWS -- the leading server virtualization and public cloud providers, respectively -- enables the combination of a wide variety VMware tools and interfaces with the flexibility and power of the AWS cloud.
AWS provides an elastic, bare metal infrastructure on top of which VMware positions its SDDC stack, which includes NSX, vSphere and vSAN.
Running VMware workloads on the AWS cloud in this elastic, bare metal structure enables workloads to request more capacity as needed through an API.
Customers can manage clusters in their own data centers and clusters running in VMware Cloud on AWS from the same interface in vCenter.
VMware sells and supports VMware Cloud on AWS as a VMware cloud service. Customers don't need an account with AWS, nor do they need significant knowledge of how AWS works.
VMware Cloud on AWS debuted as a technical preview in October 2016 and became generally available in August 2017. VMware Cloud on AWS follows a number of other partnerships between VMware and cloud providers, including IBM and Microsoft.
VMware Cloud on AWS use cases
Most use cases for VMware Cloud on AWS emerge from its ability to extend data centers while maintaining private clouds and on-premises infrastructures. Primary purposes include workload Migration, testing and development, disaster recovery, and data center consolidation and migration.
VMware Cloud on AWS enables the migration of on-premises workloads to the public cloud with tools similar to the ones IT administrators use in on-premises data centers. Organizations can migrate applications, refresh or improve a data center's infrastructure, move completely to the cloud or allocate additional capacity.
The ability to expand the scope of data centers also creates a use case for building environments to support testing and development. The cost of VMware Cloud on AWS can make it impractical as a dedicated testing platform, but it can provide space for dev/test sites to share with production applications.
Organizations can also use VMware Cloud on AWS as a disaster recovery tool. Because VMware Cloud on AWS uses VMware's existing tools and interfaces, it can offer a smooth replacement of backup data centers. Due to the geographic scope of AWS, VMware Cloud on AWS also enables the movement of workloads to areas that are safe from local threats.
VMware Cloud on AWS aids the consolidation and migration of data centers, which can otherwise be risky and costly. The integrated management between VMware services and AWS infrastructure enables the movement of applications from data centers to AWS hosts without the burden of incorporating new tools and interfaces. Customers must configure any newly provisioned environments, however, which will include setting up resource pools and high availability.
Major features of VMware Cloud on AWS
VMware Cloud on AWS makes VMware NSX practical for organizations where staff members have little network virtualization experience. With VMware Cloud on AWS, administrators can configure numerous aspects of their networks, such as firewall rules and logical networks, without needing to know NSX.
VMware Cloud on AWS features Elastic Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS), an adaptation of VMware's on-premises DRS, which enables policy-level control of workload balancing. Customers can set policies for the automatic addition or deletion of hosts, and for the balancing of workloads when utilization crosses a chosen point. If utilization exceeds capacity, VMware Cloud on AWS can add more; if utilization decreases, it can return hosts to save money.
VMware Cloud on AWS enables the rapid allocation of hosts, similar to AWS instances, such that new customers can get a host in about two hours. The addition and removal of hosts after that initial creation can take only minutes.
VMware Cloud on AWS pros and cons
The primary benefits of VMware Cloud on AWS result from data center extensibility as made possible by an interface that integrates AWS scale with VMware tools.
VMware Cloud on AWS provides a familiar interface for administrators who are familiar with VMware products. It runs new hosts and added capacity in vCenter alongside other hosts in the data center. The rest of VMware's SDDC stack is similarly available for use and the integration of these tools provides for simple, efficient management across private and public workloads.
VMware Cloud on AWS also helps with the deployment and integration of different applications and services. By running VMware workloads alongside AWS services, administrators can use numerous AWS tools, such as Lambda, DynamoDB and Relational Database Service in a variety of hybrid purposes.
The primary hindrance to VMware Cloud on AWS adoption is cost.
VMware Cloud on AWS, like many other cloud providers, bills its customers for reserved capacity, not for what they actually use. This can become costly for organizations hoping to reserve capacity for disaster recovery because they reserve -- and pay for -- space they hope they won't need.
To get an idea of the total cost of ownership (TCO), customers must compare VMware Cloud on AWS's various pricing plans to on-premises options and take into account the costs of their particular facilities. Application and OS licensing costs are similar between VMware Cloud on AWS and on-premises, but the costs of an on-demand cloud service versus capital-intensive hardware will vary between data centers depending on staff, budget, and unique networking and maintenance needs.
Pricing plans and licensing
VMware modelled its pricing plans on AWS's, which offer on-demand and reserve pricing plans.
VMware Cloud on AWS is priced as a consumption-based cloud service. VMware charges based on three plans, all of which include support, configuration and patch management.
One option is hourly and on-demand, which enables customers to create hosts and pay for the hours used for as many VMs as needed. The on-demand cost is $8.37 per host, per hour.
Purchased hosts have two CPUs, 36 cores, 72 hyper-threads, 512 Gibibyte RAM and 10.7 TB of flash storage. VMware Cloud on AWS is cluster-based and requires a minimum purchase of four hosts. This means that the entry, on-demand cost is $33.48 per hour for all four hosts.
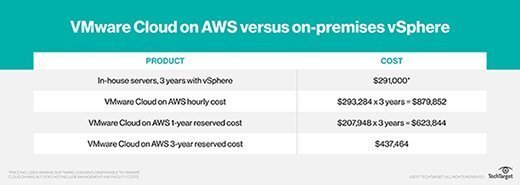
This will cost about $267.84 for an eight-hour work day, $1,339.20 for a 40-hour work week and $5,624.64 for an entire week, including off hours. For a year of on-demand service, the price is about $293,285, but the reserved pricing model offers a cheaper price at that span if purchased up front.
A contract for a yearlong, reserved instance costs $51,987 per host. A contract for three years of reserved capacity costs $109,366 per host and saves about 50% in comparison to the on-demand price. VMware estimates that the TCO for VMWare Cloud on AWS with the three-year contract is up to $0.09 per VM, per hour.
VMware Cloud on AWS has separate charges for data transfers and AWS egress fees. In the latter case, customers will incur a cost to pull workloads out of the AWS cloud, which can create workload lock-in. VMware offers add-ons that will increase the per-host cost if purchased, such as VMware Site Recovery, which offers disaster recovery as a service. Some businesses qualify for VMware's Hybrid Loyalty Program, which could garner a discount.








